
Risk Based Monitoring Toolbox
Introduction
The Risk-Based Monitoring Toolbox provides information on tools available for risk assessment, monitoring and study conduct, the institutions where they are used, and other relevant details such as links and user feedback. The goal is to enable researchers to create risk-based strategies that are appropriate for their study needs.
Launched end 2015, the Toolbox was created following a systematic literature review on current practices and recommendations as well as a survey of clinical trial units (CTUs). The survey identified existing risk-adapted monitoring tools, risk evaluation methods, and monitoring strategies.
Click on the chapters below to find relevant information
Risk-based monitoring in clinical trials is the practice of assessing the risks of a clinical study and using this information to decide which monitoring effort is most appropriate. Traditionally, Source Document Verification is carried out on 100% of data and frequent onsite visits are required. In a risk-based approach, depending on the strategy, Source Document Verification may be carried out only for certain targeted data or some data points may be verified only after a predefined trigger, such as an event occurring at a site or a specific metric being reached. Risk-based monitoring can lead to more efficient use of resources without reduction in data quality.
Scope of Monitoring
Monitoring is the act of overseeing the progress of a clinical trial and ensuring that it is conducted, recorded and reported in accordance with the protocol, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and the applicable regulatory requirement(s) (European Medicines Agency 2002). The purpose of trial monitoring is to verify that the rights and well-being of human subjects are protected and the reported trial data are accurate, complete, and verifiable from source documents.
However, a broader definition of trial monitoring includes strategies that enhance trial oversight during the design, execution and analysis stages (Baigent 2008). Also, monitoring activities are not limited to onsite visits but must be understood as all onsite and central activities dealing with checks of data and procedures as well as with the overall surveillance and stimulation of the trial progress.
The Risk-Based Approach: New Paradigm, Big Challenge
The European regulation on clinical trials, as well as guidelines from competent authorities, now require the use of the risk-based approach for many aspects of trial conduct, among which monitoring.
However, the approach is not easily grasped, and no instruction manual has been provided. Furthermore, the very concept of risk-based approach implies that the chosen strategy is adapted to local and trial-specific context. So there is no "one-fits-all" model anymore, and most stakeholders are at a loss to define a relevant trial-specific strategy.
The Toolbox: Objective and Content
We set up this toolbox gathering risk-based tools and strategies already proposed and/or validated together. The visitor may compare different tools, appraise their scope, specificities, strengths and weaknesses, and choose those fit to build a specific monitoring strategy.
We considered any type of tool: standard document, checklist, procedure, software, device, etc. However, commercial tools, information technology, and data management tools were not considered because they come under data management more than monitoring activities, and information on these tools may be found easily on the Internet.
Tools Identification and Description
Tools were detected through a systematic review of the published literature (January 2006 to June 2015), a search of the grey literature, and a survey among clinical trial units and academic sponsors within the ECRIN network (2013). The objective was to identify current state of practice and recommendations in clinical trials, key elements of monitoring, risk assessment tools and risk-adapted monitoring tools.
Tools are not directly available from the toolbox. Each tool is described through its scope, format and purpose. Contact information of the team having developed the tool, or reference of published article, is also provided.
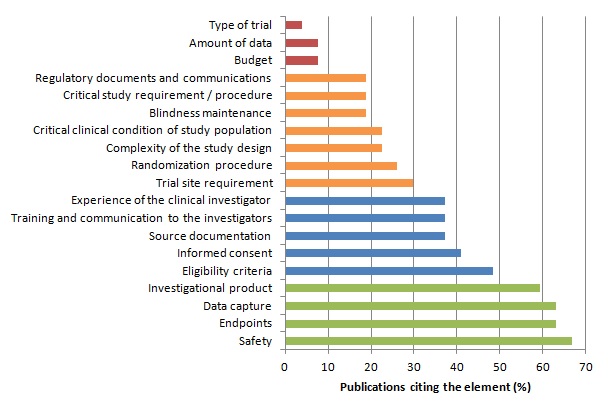
Among the different steps of a clinical trial, some may be more crucial for patients’ safety and the validity of study results.
We assumed that the importance of an element is reflected through the proportion of publications considering this element in monitoring strategies or quality control methods.
We identified 27 publications (Bakobaki 2011; Baigent 2008; Brosteanu 2009; Journot 2011; Kirwan 2008; Méthot 2012; Sandman 2006; Williams 2006; Bertoye 2006; Cooley 2010; De 2011; Grieve 2012; Kirkwood 2013; Matthews 2011; Ansmann 2013; Venet 2012; Macefield 2012; Tudur-Smith 2014; Graham 2012; Heels-Ansdell 2010; McBee 2012; Novik 2014; Shugarts 2012; CTTI (Morrisson 2010; Morrisson 2011); FDA 2013; EMA; MRC/DH; MRC/DH/MHRA) reporting analyses of monitoring strategies and/or methods for quality control of clinical trial data and procedure. These publications differed significantly in the purpose addressed and the topic discussed. However the identified key elements are reported in the table and figure below.
Distribution of Key Elements of Monitoring :
The risk-based approach relies on the identification and assessment of risk(s).
Risk is defined by ISO 31000 standard as "the effect of incertitude on objectives". In clinical research, the considered risks are always negative, so risk is best characterised by the occurrence of a negative event.
For years, risk has been interpreted as risk for patient's safety or rights only. However, other types of risk should be considered: for the participant in the study, the institutions and teams in charge of the study conduct, the governance structures, the target population, and the public health stakeholders, etc.
| Topic | Validation | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| ADAMON Risk Scale Author: TMF (Telematikplattform für Medizinische Forschungsnetze e.V.) Risk category: Patient's safety and rights from interventions and investigations, validity of trial results Research category: Non-commercial trial Format: 3-level scale (comparable to / higher than / markedly higher than that of standard medical care) based on intervention characteristics and analysis of further indicators for patient-related risks and risks for the validity of trial results Purpose: Risk assessment and adaptation of onsite monitoring intensity and focus |
Reproducibility study on 53 trial protocols (Brosteanu et al, 2009) | Access tool |
| Guidance Document on Risk Assessment Author: ECRIN network Risk category: Any Research category: Any Format: List of 19 study characteristics, split into 5 topics (study participants, validity of study results, study organisation, study governance, impact of study results on target population and public health) to be considered during risk assessment, with comments and examples Purpose: Risk identification |
2-round Delphi consensus process by 100 experts within ECRIN network | Download here |
| Guideline on Risk Management for Clinical Research Author: F-CRIN / ECRIN networks Risk category: Any Research category: Any Format: Guideline transposing to clinical research and exemplifying the ISO 31000 standard on risk management Purpose: Risk mitigation through adaptation of study procedures, including data management, monitoring and study conduct |
Draft reviewed by experts within F-CRIN and ECRIN networks | Download here |
| Logistics / Impact / Resources Score Author: Sponsorship Quality Group of French Hospitals Risk category: Risks related to logistics, impact or resources aspects of study Research category: Any Format: To be used after patient's risk assessment through Optimon risk scale; quantitative score (0 to 40) based on logistics, impact and resource study characteristics; to be split into 3 intensity levels of monitoring (minimal / intermediate / high) Purpose: Adaptation of intensity and focus on onsite monitoring |
Feedback expected from ongoing studies | Contact: valerie.plattner@chu-lyon.f |
| MRC/DH/MHRA Joint Project - Risk-Adapted Approaches to the Management of Clinical Trials of Investigational Medicinal Products Author: MRC/MHRA/DH Risk category: Patient's safety / Any Research category: Drug trials Format: 3-level scale (comparable to / somewhat higher than / markedly higher than the risk of standard medical care) / Identification (no scoring) of risks to participants and to the reliability of results Purpose: Adaptation of intensity and focus on onsite monitoring |
Feedback expected from ongoing studies | Access tool |
| Risk-Based Monitoring Score Calculator Author: SCTO (Swiss Clinical Trials Organisation) Risk category: Patient's safety and rights from interventions and investigations Research category: Non-commercial trial Format: 3-level scale (comparable to / higher than / markedly higher than that of standard medical care) based on intervention characteristics Purpose: Adaptation of intensity and focus of onsite monitoring |
Access tool | |
| Guideline for a Coordinated GCP-Monitoring of Clinical Trials in the Nordic Countries Author: NORM (Nordic Monitoring Network) Risk category: Any Research category: Trials Format: 3-level scales for probability of occurrence and severity of consequences Purpose: Adaptation of onsite monitoring |
Feedback expected from ongoing studies | Access tool |
| OPTIMON Risk Scale Author: Bordeaux University Hospital Risk category: Patient's safety from interventions and investigations Research category: Any Format: 4-level scale (A: no or very low risk / B / C / D: highest risk) based on intervention and investigation characteristics Purpose: Adaptation of onsite monitoring |
Reproducibility evaluated on 200 study protocols with various designs, interventions and indications (Journot et al, 2009) |
On-Site Monitoring
Source Data Activities
On-site monitoring (OSM) is still associated with source data verification (SDV) as a key activity. Indeed, for long years SDV was deemed the most important procedure for achieving high data quality. However, the value of extensive SDV has been questioned in the last years, and there is an increasing body of evidence in the literature showing that 100% SDV is a very costly but not very effective measure in terms of high data quality.
Several authors have investigated the impact of data corrections following SDV; their results are summarized e.g. in the survey of (Tantsyura et al. 2015a).
Sheetz et al (Sheetz et al. 2014) present a retrospective analysis of 1168 clinical trials performed by a total of 53 pharmaceutical sponsors. In all trials, electronic data capture was used. The trials cover phases I to IV and a broad range of indications. The authors show that only 3.7% of all data captured where corrected after initial entering. From these, only 1/3 was corrected due to SDV findings, while the others corrections where performed following automatically generated queries or queries raised by data management. That means that only 1.1% of all data had to be corrected due to SDV findings. This in line with Mitchel et al (Mitchel et al. 2011), who reported a rate of data corrections of 6.2%, from which 71% were due to data entry errors. These corrections had only minimal impact on the means of the primary variables. However, a slight increase in variance was seen with uncorrected data, such that an increase of 1% in the sample size would have been enough to counteract the loss of power due to uncorrected data. Tudur Smith et al (Tudur Smith et al. 2012) present an analysis based on a non-commercial cancer trial comparing two treatments in over 500 patients in 75 UK trial sites. The trial was not blinded, and paper CRF were used for documentation. The authors report discrepancy rates of about 7.8% for the primary endpoint survival and as high as 24.8% for the secondary endpoint progression free survival. However, these discrepancies were at random and had no impact on the study results, with superimposable Kaplan-Meier curves and only slightly different hazard ratios. It is of interest to mention that in this trial, the authors describe a discrepancy rate of 85.6% in the subjective outcome “objective response”. With respect to this finding, the authors conclude that “an independent blinded review committee and tracking system to monitor missing CT scan data could be more efficient than SDV”.
It should be stressed here that the authors cited above do not question the value of on-site monitoring visits in general. It is only the relevance and efficiency of searching for transcription errors that is challenged. For example, Sheetz et al (Sheetz et al. 2014) report that 11% of the adverse events and 3.6% of the serious adverse events were detected by source data review.
| Topic | Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Four Strategies for Reduced SDV Random SDV approach: Screening and baseline visits are randomly monitored at 20%. Based on the quality assessment from these initial visits, the remaining visits are monitored at 20% if the quality is good and at 100% if the quality is poor. Declining SDV approach: Screening and baseline visits are monitored at 100%. After the error rate has been determined, the monitoring rate declines to 20% if the quality is good and stays at 100% if the quality is poor. 3-tiered approach: forms are classified into 3 tiers (Tier 1 - highest importance, forms monitored at 100%; Tier 2 monitored at 20%; Tier 3 not monitored at all). Mixed approach: Forms are classified as either critical or noncritical. During the screening and baseline visits, all forms are monitored at 100%. In subsequent visits, critical forms are monitored at 100%, while noncritical forms are not monitored at all |
Evaluated retrospectively in 30 finished clinical trials by simulation of the percentage of errors potentially detected by each strategy (Nielsen et al. 2014). Nielsen et al conclude that the mixed approach strategy is the best option in terms of detection of critical errors in relation to the operating expense of SDV. |
Tantsyura et al. 2010 |
| Statistical Sampling Method for SDV Upfront, an acceptable quality Level (AQL, i.e. acceptable rate of items with discrepancies between source and CRF) has to be decided upon. Given the AQL, the number of data items at each patient visit, and the number of patient visits that took place since last monitoring, the number of patient visits to be monitored as well as the number of acceptable errors for the next monitoring visit is determined. If SDV shows a number of errors lower than the acceptable threshold, it may be concluded that the true error rate lies below the AQL. |
Simulation studies to investigate the potential impact of the method on data quality are provided. | Grieve 2012 |
| On-Demand Query-Driven SDV The authors aim to provide an efficient and scientifically grounded model for SDV, by integrating SDV in the query management process. Basically, the authors propose to classify data in critical and non-critical. In critical data which may be surveyed by edit checks, statistical data surveillance or medical review, SDV should be performed on queries only. In all noncomputerizable critical data (e.g. eligibility criteria, protocol violations) 100% SDV should be performed. Non-critical data should be surveyed by edit checks only. |
The proposal is based on extensive literature research, but its efficacy has not yet been assessed. | Tantsyura et al. 2015b |
| Source Data Review Source Data Review is defined as a “review of source data for protocol compliance, quality of documentation, as well as site processes in contrast to transcription checking, referred to as Source Data Verification (SDV)”. |
TransCelerate BioPharma Inc 2013 Henderson 2013 |
Training and Other On-Site Activities
As stated by Baigent et al (Baigent et al. 2008), “on-site monitoring should be … regarded as "mentoring", providing opportunities for training and supporting study staff”. In this section, two papers describing on-site activities beyond SDV are reviewed.
| Topic | Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Site Monitoring Process Using Peer Reviewers to Improve Staff Training, Site Performance, Data Collection and GCP Compliance Procedure for annual site visits performed by an experienced team, with detailed description of proposed on-site activities |
Implementation in a large multicentre trial is described, demonstrating a decrease of findings with ongoing site visits. | Lane et al. 2011 |
| Clinical Trial Educator (CTE) Program – to accelerate enrolment Program involving regular site visits by specifically trained personnel in order to train and educate investigators and site staff with respect to recruitment challenges. |
Non-randomised evaluation of the programme in a large-scale trial showed significantly better recruitment rates in sites visited by a CTE, | Kendall et al. 2012 Central Monitoring |
Central Monitoring
Central monitoring or central statistical monitoring comprise all activities for the surveillance of a clinical trial which may be performed centrally, including data management checks, surveillance by statistical description or analysis, medical review, core labs and review committees for the central assessments of e.g. scans or clinical endpoints.
Remote Monitoring
With rapidly developing technologies, remote access to source data is an option sometimes discussed as an alternative to on site monitoring. However, data protection issues may pose serious problems with this approach.
| Topic | Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Source Data Verification (SDV) Via Remote Electronic Access for Monitors to Electronic Source Data Limitation: approach may be hampered by restrictive access policies of the institutions to which trial sites belong. |
Randomised comparison of remote SDV with on-site SDV. In this pilot study, more than 99% of data items could be successfully monitored remotely. The time required per item monitored was higher for remote SDV, but this may be acceptable given the spared travel time. | Mealer et al. 2013 |
| Procedure for Remote Pre-Enrolment Checking of Consent Forms | Efficiency to reduce nonconformity of the informed consent process with regulatory requirements was prospectively assessed in five trials. | Journot et al. 2013 |
Central Statistical Monitoring
The potential of central statistical monitoring to detect erroneous data and deficient trial sites has been demonstrated e.g. by Bakobaki et al (Bakobaki et al. 2012) and Lindblad et al ( (Lindblad et al. 2014). Bakobaki and colleagues examine a sample of on site monitoring reports, and find that about 95% of all findings could have been identified by means of central monitoring. Lindblad et al analyse data submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) by clinical trial sponsors. They show that “systematic central monitoring of clinical trial data can identify problems at the same trials and sites identified during FDA site inspections”.
Recently, a differentiation between central monitoring using key risk indicators pre-identified by prior risk assessment and “centralized statistical monitoring” has been proposed (Buyse M 2014). In this proposal, centralized statistical monitoring is characterised as the application of advanced statistical and bioinformatics methods on all available clinical trial data without any prioritisation (Venet et al. 2012). However, we do not follow this distinction, because in both cases, statistical techniques are required to make best use of the available information. The two approaches should be considered as complementary. Thorough risk assessment lead to identification of anticipated study specific hazards, which have to be adequately surveyed. The central statistical monitoring techniques proposed by Venet et al (Venet et al. 2012) may help to detect unexpected problems, but have a low specificity and may detect issues of low relevance for the integrity of the trial.
| Topic | Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Statistical Techniques to Detect Unusual or Unexpected Patterns in Data such as outliers, inliers, overdispersion, underdispersion, correlations or lack thereof, digit preferences, round number preferences, repeated measurement issues, calendar time features. | Used e.g. in (Al-Marzouki et al. 2005) (Kirkwood et al. 2013) to detect data fabrication or data errors | Buyse et al. 1999 |
| Graphical and Statistical Methods Suitable for Discrete Outcomes, e.g. for questionnaire data. The methods exploit the underlying correlation structure of the data. | Suitability assessed using a data set from a psychiatric trial. | Taylor et al. 2002 |
| Early Identification of Risks Using Analysis of Key Performance Indicators A set of key performance indicators (KPI) for clinical as well as for operational aspects is proposed. The analysis of these KPIs leads to identification of trial sites at risk for non-compliance |
Proof-of-concept of the method using data from two representative trials | Djali et al. 2010 |
| Cluster Analysis Methods for Identification of Trial Sites with Unexpected Patterns Between Sets of Recorded Variables Three clustering patterns, angular, neighbourhood and repeated measurements clustering, with corresponding simple and efficient test statistics are proposed. |
Application of the method to a 12-week multicentre study with known deficient trial sites. Simulation study for validation of the effectiveness |
Wu und Carlsson 2011 |
| Identification of Systematic Problems in Continuous Variables Use of intraclass correlation coefficients to assess periodically during data collection if the measurements in a single centre differ from others. |
Illustration in a multicentre cluster-randomised trial | Guthrie et al. 2012 |
| Identification of Extreme Centres by Bioinformatics Approaches Statistical approach based on a large number of statistical tests performed on all variables collected in the database, in order to identify centres that differ from the others. The tests generate a high-dimensional matrix of p -values, which can be analysed by statistical methods and bioinformatics tools to identify extreme centres. |
Typical findings are illustrated. Used e.g. in a case study (Timmermans et al. 2015a). Further examples in ((Timmermans et al. 2015b) |
Venet et al. 2012 |
| Risk Scores to Identify Fabricated Data Within a Multicentre Trial A database from a multicentre trial in which data from 9 of 109 centres were documented to be fabricated was used to identify five different risk scores with the ability to discriminate well between centres with and without fabricated data (area under the curve values ranged from 0.90 to 0.95). Limitations: so far for specific cardiovascular trials only. |
Validation for false-positive rate using an independent multicentre trial database that contained no data fabrication | Pogue et al. 2013 |
| Central Statistical Monitoring of Multicentre Clinical Trials Detection procedure based on a linear mixed-effects model to detect location differences between each centre and all other centres in the case of a continuous variable |
Illustration using data from two multicentre clinical trials. | Desmet et al. 2014 |
| Central Data Monitoring in Clinical Trials | Monitoring Platform of the SCTO |
Case Examples
In this section we present some case examples for the implementation of risk-based approaches.
| Topic | Reference |
|---|---|
| Quality Management Tools and Procedures Implemented in a Large Multicentre Trial Description of the tools and procedures, and of the experiences gained during trial conduct |
Kirwan et al. 2008 |
| Measures for Prevention of Drop-outs In case of trials with an expected high rate of drop-out or non-compliance, data from previous trials may be used to identify patient subgroups more likely to drop-out. Proactive measures are presented focussing of the patients at risk for drop-out. These measures included e.g. pre-trial-training, opt-in text-messaging for trial visit reminders, alerting sites to subjects who are late for a clinic visit, but also continued tracking by the statistics group of dropout rates for ongoing new trials, with prompt escalation if significant numbers of potentially avoidable dropouts are observed, to investigate and address (if possible) root causes. |
Hughes et al. 2012 |
| Implementation of Central and Statistical Monitoring The methods implemented for central and statistical monitoring in a large multicentre trial are described, as well as their use to target on-site visits. |
Edwards et al. 2013 |
| Risk-Proportionate Clinical Trial Monitoring Approach in a Non-Commercial Clinical Trial Unit With examples of tools for central monitoring |
Tudur Smith et al. 2014 |
Trial Oversight
Different types of oversight committees may be installed in clinical trials, depending on the size and complexity of the trial and the study population involved (Baigent et al. 2008).
We focus here on independent Data Monitoring Committees (DMC, synonyms e.g. Data Monitoring and Safety Board, Data Safety Monitoring Board), and list publications dealing with considerations and procedures which may be of use when installing a DMC.
| Topic | Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Charter for Clinical Trial Data Monitoring Committees Proposal for a template for a charter for DMCs, based on systematic reviews of DMCs and small group processes in decision making; surveys of reports of RCTs, recently completed and ongoing RCTs, and the policies of major organisations connected with RCTs; detailed case studies of four DMCs that faced difficult decisions; and interviews with experienced DMC members. |
Damocles 2005 | |
| Issues in Data Monitoring and Interim Analysis of Trials This comprehensive survey addresses practical questions related with the implementation of a DMC. |
Grant et al. 2005 | |
| Presentation of Real-Life Challenges Faced by Clinical trial DTta Monitoring Committees (DMCs) Some real-life challenges faced by DMCs in the decision to stop for early benefit or early harm are presented and discussed. The aim is to clarify “some of the controversial issues that relate to both statistical stopping boundaries and DMC decision-making” |
Pocock 2006 | |
| Three Statistician Models in Case of Interim Analyses A workflow is presented on how to practically implement the three statistician models in the event of trials with unblinded interim analyses supervised by a DMC |
Baggs et al. 2008 |
Al-Marzouki, Sanaa; Evans, Stephen; Marshall, Tom; Roberts, Ian (2005): Are these data real? Statistical methods for the detection of data fabrication in clinical trials. In: BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 331 (7511), S. 267–270. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.331.7511.267.
Ansmann E.B, Hecht A, Henn D.K, Leptien S, Stelzer HG. The future of monitoring in clinical research – a holistic approach: Linking risk-based monitoring with quality management principles. GMS German Medical Science 2013; 11:1-8.Baggs, G.; Seth, A.; Oliver, J. S.; Jones, W. M.; liu, L.; Toth, S. M. (2008): Monitoring Clinical Trial Data Using an Unblinded Industry Statistician. In: Drug Information Journal 42, S. 193–199. Online verfügbar unter doi:10.1177/009286150804200211.
Baigent, Colin; Harrell, Frank E.; Buyse, Marc; Emberson, Jonathan R.; Altman, Douglas G. (2008): Ensuring trial validity by data quality assurance and diversification of monitoring methods. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 5 (1), S. 49–55. DOI: 10.1177/1740774507087554.
Bakobaki, Julie M.; Rauchenberger, Mary; Joffe, Nicola; McCormack, Sheena; Stenning, Sally; Meredith, Sarah (2012): The potential for central monitoring techniques to replace on-site monitoring: findings from an international multi-centre clinical trial. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 9 (2), S. 257–264. DOI: 10.1177/1740774511427325.
Bertoye, P. H., S. Courcier-Duplantier, et al. Adaptation of the application of good clinical practice depending on the features of specific research projects. Therapie 2006; 61(4): 279-85, 271-7.
Brosteanu, Oana; Houben, Peggy; Ihrig, Kristina; Ohmann, Christian; Paulus, Ursula; Pfistner, Beate et al. (2009): Risk analysis and risk adapted on-site monitoring in noncommercial clinical trials. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 6 (6), S. 585–596. DOI: 10.1177/1740774509347398.
Buyse, M.; George, S. L.; Evans, S.; Geller, N. L.; Ranstam, J.; Scherrer, B. et al. (1999): The role of biostatistics in the prevention, detection and treatment of fraud in clinical trials. In: Statistics in medicine 18 (24), S. 3435–3451.
Buyse M (2014): Centralized Statistical Monitoring As a Way to Improve the Quality of Clinical Data. In: Applied Clinical Trials. Online verfügbar unter http://www.appliedclinicaltrialsonline.com/centralized-statistical-monitoring-way-improve-quality-clinical-data?pageID=1.
Clinical Trials Transformation Initiative. https://www.ctti-clinicaltrials.org/
Cooley S, S. B. Triggered monitoring. Applied clinical trials online.2010
DAMOCLES (2005): A proposed charter for clinical trial data monitoring committees: helping them to do their job well. Helping them to do their job well. In: Lancet (London, England) 365 (9460), S. 711–722. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17965-3.
De, S. Hybrid approaches to clinical trial monitoring: Practical alternatives to 100% source data verification. Sheetz, N.; Wilson, B.; Benedict, J.; Huffman, E.; Lawton, A.; Travers, M. et al. (2014): Evaluating Source Data Verification as a Quality Control Measure in Clinical Trials. In: Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science 48 (6), S. 671–680. DOI: 10.1177/2168479014554400.
Desmet, L.; Venet, D.; Doffagne, E.; Timmermans, C.; Burzykowski, T.; Legrand, C.; Buyse, M. (2014): Linear mixed-effects models for central statistical monitoring of multicenter clinical trials. In: Statistics in medicine 33 (30), S. 5265–5279. DOI: 10.1002/sim.6294.
Djali, S.; Janssens, S.; van Yper, S.; van Parijs, J. (2010): How a Data-Driven Quality Management System Can Manage Compliance Risk in Clinical Trials. In: Drug Information Journal 44, S. 359–373.
Edwards, Phil; Shakur, Haleema; Barnetson, Lin; Prieto, David; Evans, Stephen; Roberts, Ian (2013): Central and statistical data monitoring in the Clinical Randomisation of an Antifibrinolytic in Significant Haemorrhage (CRASH-2) trial. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 11 (3), S. 336–343. DOI: 10.1177/1740774513514145.
European Commission. Enterprise and Industry Directorate-General. Draft guidance on ‘specific modalities’ for non-commercial clinical trials referred to in Commission Directive 2005/28/EC laying down the principles and detailed guidelines for good clinical practice.http://ec.europa.eu/health/files/pharmacos/docs/doc2006/07_2006/guide_noncommercial_2006_07_27_en.pdf
European Medicines Agency (2002). Note for Guidance on Good Clinical Practice.http://www.emea.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500002874.pdf.
European Medicines Agency (2013): Reflection paper on risk-based quality management in clinical trials. Online verfügbar unter https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-risk-based-quality-management-clinical-trials_en.pdf.
Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry Oversight of Clinical Investigations — A Risk-Based Approach to Monitoring.
Graham, L., S. Anwar, et al. Risk management of non-CTIMP trials: Focus on complex intervention trials. Clinical Trials 2012; 9(4): 517.
Grieve, A. P. (2012): Source Data Verification by Statistical Sampling. Issues in Implementation. In: Drug Information Journal 46 (3), S. 368–377. DOI: 10.1177/0092861512442057.
Guthrie, Lauren B.; Oken, Emily; Sterne, Jonathan A. C.; Gillman, Matthew W.; Patel, Rita; Vilchuck, Konstantin et al. (2012): Ongoing monitoring of data clustering in multicenter studies. In: BMC medical research methodology 12, S. 29. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-29.
Heels-Ansdell, D., S. Walter, et al. Central statistical monitoring of an international thromboprophylaxis trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2010; 181(1).
Henderson, L. (2013): Distinct RBM Divisions: source document verification and source data review. In: Applied Clinical Trials July.
Hughes, Sara; Harris, Julia; Flack, Nancy; Cuffe, Robert L. (2012): The statistician's role in the prevention of missing data. In: Pharmaceutical statistics 11 (5), S. 410–416. DOI: 10.1002/pst.1528.
Journot V, Pignon JP, Gaultier C, et al. On behalf of the Optimon Collaborative Group. Validation of a risk assessment scale and a risk-adapted monitoring plan for academic clinical research studies – The Pre-Opti¬mon
Journot, Valérie; Pérusat-Villetorte, Sophie; Bouyssou, Caroline; Couffin-Cadiergues, Sandrine; Tall, Aminata; Chêne, Geneviève (2013): Remote pre enrollment checking of consent forms to reduce nonconformity. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 10 (3), S. 449–459. DOI: 10.1177/1740774513480003.
Kendall, Brigitte; Städeli, Reto; Schegg, Belinda; Olbrich, Martin; Chen, Edmond; Harmelin-Kadouri, Rona et al. (2012): Clinical Trial Educator program - a novel approach to accelerate enrollment in a phase III International Acute Coronary Syndrome Trial. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 9 (3), S. 358–366. DOI: 10.1177/1740774512440760.
Kirkwood, Amy A.; Cox, Trevor; Hackshaw, Allan (2013): Application of methods for central statistical monitoring in clinical trials. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 10 (5), S. 783–806. DOI: 10.1177/1740774513494504.
Kirwan, Bridget-Anne; Lubsen, Jacobus; Brouwer, Sophie de; van Dalen, Frederik J.; Pocock, Stuart J.; Clayton, Tim et al. (2008): Quality management of a large randomized double-blind multi-centre trial: the ACTION experience. In:Contemporary clinical trials 29 (2), S. 259–269. DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2007.10.001.
Lane, J. Athene; Wade, Julia; Down, Liz; Bonnington, Susan; Holding, Peter N.; Lennon, Teresa et al. (2011): A Peer Review Intervention for Monitoring and Evaluating sites (PRIME) that improved randomized controlled trial conduct and performance. In: Journal of clinical epidemiology 64 (6), S. 628–636. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.10.003.
Lindblad, Anne S.; Manukyan, Zorayr; Purohit-Sheth, Tejashri; Gensler, Gary; Okwesili, Paul; Meeker-O'Connell, Ann et al. (2014): Central site monitoring: results from a test of accuracy in identifying trials and sites failing Food and Drug Administration inspection. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 11 (2), S. 205–217. DOI: 10.1177/1740774513508028.
Macefield, R. C., A. D. Beswick, et al. A systematic review of on-site monitoring methods for health-care randomised controlled trials. Clin Trials 2013; 10(1): 104-24.Mealer, Meredith; Kittelson, John; Thompson, B. Taylor; Wheeler, Arthur P.; Magee, John C.; Sokol, Ronald J. et al. (2013): Remote source document verification in two national clinical trials networks: a pilot study. In: PloS one 8 (12), S. e81890. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081890.
McBee, W. L., S. Schenning, et al. Effective monitoring strategies in a long-term clinical trial with varying levels of clinic staff knowledge: The AREDS2 experience. Clin Trials 2012; 9(4): 462.
Méthot J, Brisson D, Gaudet D. On-site management of investigational products and drug delivery systems in conformity with Good Clinical Practices (GCPs). Clin Trials 2012; DOI: 10.1177/1740774511431280
Mitchel, J. T.; Kim, Y. J.; Choi J; Park, G.; Cappi, S.; Horn, D. et al. (2011): Evaluation of Data Entry Errors and Data Changes to an Electronic Data Capture Clinical Trial Database. In: Drug Information Journal 45, S. 421–430.
Morrison, B., J. Neaton, et al. A CTTI survey of current monitoring practices. Clinical Trials 2010; 7(4): 464.
Morrison BW, Cochran CJ, White JG. Monitoring the quality of conduct of clinical trials: a survey of current practices. Clin Trials 2011; 8: 342-9
MRC/DH Joint project to codify good practice in publicly-funded UK clinical trials with medicines http://www.ct-toolkit.ac.uk
MRC/DH/MHRA Joint Project. Risk-adapted Approaches to the Management of Clinical Trials of Investigational Medicinal Products (Version: 10th October 2011) http://www.mhra.gov.uk/home/groups/l-ctu/documents/websiteresources/con111784.pdf
Nielsen, E.; Hyder, D.; Deng, C. (2014): A Data-Driven Approach to Risk-Based Source Data Verification. In: Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science 48 (2), S. 173–180. DOI: 10.1177/2168479013496245.
Novik, Y., L. Fleming, et al. Monitoring data and compliance in institutional cancer trials: Consistent quality improvement by internal peer audit process. Clinical Trials 2010; 7(4): 430.
Pocock, Stuart J. (2006): Current controversies in data monitoring for clinical trials. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 3 (6), S. 513–521. DOI: 10.1177/1740774506073467.
Pogue, Janice M.; Devereaux, P. J.; Thorlund, Kristian; Yusuf, Salim (2013): Central statistical monitoring: detecting fraud in clinical trials. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 10 (2), S. 225–235. DOI: 10.1177/1740774512469312.
Sandman L, Mosher A, Khan A. Quality assurance in a large clinical trials consortium: The experience of the Tuberculosis Trials Consortium. Contemp Clin Trials 2006; (27): 554–560
Shugarts, P., R. Kozloff, et al. Risk-based approach to monitoring: The way of the future. Clinical Trials 2012; 9(4): 462.Grant, A.; Altman, D.; Babiker, A.; Campbell, M.; Clemens, F.; Darbyshire, J. et al. (2005): Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials. In: Health Technol Assess 9 (7). DOI: 10.3310/hta9070.
Tantsyura, V.; Dunn, I. M.; Fendt, K.; Kim, Y. J.; Waters, J.; Mitchel, J. (2015a): Risk-Based Monitoring. A Closer Statistical Look at Source Document Verification, Queries, Study Size Effects, and Data Quality. In: Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science. DOI: 10.1177/2168479015586001.
Tantsyura, V.; Dunn, I. M.; Waters, J.; Fendt, K.; Kim, Y. J.; Viola, D.; Mitchel, J. (2015b): Extended Risk-Based Monitoring Model, On-Demand Query-Driven Source Data Verification, and Their Economic Impact on Clinical Trial Operations. In:Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science. DOI: 10.1177/2168479015596020.
Tantsyura, Vadim; Grimes, Imogene; Mitchel, Jules; Fendt, Kaye; Sirichenko, Sergiy; Waters, Joel et al. (2010): Risk-Based Source Data Verification Approaches: Pros and Cons. In: Drug Information Journal 44, S. 745–756. Online verfügbar unter doi:10.1177/009286151004400611.
Taylor, R.; McEntegart, D.; Stillman, E. (2002): Statistical techniques to detect fraud and other data irregularities in clinical questionnaire data. In: Drug Information Journal 36, S. 115–125.
Timmermans, Catherine; Doffagne, Erik; Venet, David; Desmet, Lieven; Legrand, Catherine; Burzykowski, Tomasz; Buyse, Marc (2015a): Statistical monitoring of data quality and consistency in the Stomach Cancer Adjuvant Multi-institutional Trial Group Trial. In: Gastric cancer : official journal of the International Gastric Cancer Association and the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. DOI: 10.1007/s10120-015-0533-9.
Timmermans, Catherine; Venet, David; Burzykowski, Tomasz (2015b): Data-driven risk identification in phase III clinical trials using central statistical monitoring. In: International journal of clinical oncology. DOI: 10.1007/s10147-015-0877-5.
TransCelerate BioPharma Inc (2013): TransCelerate-RBM-Position-Paper-FINAL-30MAY2013. Online verfügbar unter http://www.transceleratebiopharmainc.com/, zuletzt geprüft am 08.10.2015.
Tudur Smith, Catrin; Stocken, Deborah D.; Dunn, Janet; Cox, Trevor; Ghaneh, Paula; Cunningham, David; Neoptolemos, John P. (2012): The value of source data verification in a cancer clinical trial. In: PloS one 7 (12), S. e51623. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051623.
Tudur Smith C, Williamson P, Jones A, Smyth A, Langton Hewer S, Gamble C (2014): Risk-proportionate clinical trial monitoring: an example approach from a non-commercial trials unit. In: Trials 15, S. 127. DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-127.
US Food and Drug Administration (2013): Guidance for Industry Oversight of Clinical Investigations — A Risk- Based Approach to Monitoring. Online verfügbar, zuletzt geprüft am 06.10.2015.
Venet D, Doffagne E, Burzykowski T, Beckers F, Tellier Y, Genevois-Marlin E et al. (2012): A statistical approach to central monitoring of data quality in clinical trials. In: Clinical trials (London, England) 9 (6), S. 705–713. DOI: 10.1177/1740774512447898.
Williams GW. The other side of clinical trial monitoring; assuring data quality and procedural adherence. Clin Trials 2006 3: 530-7
Wilson, B.; Provencher, T.; Gough, J.; Clark, S.; Abdrachitov, R.; Roeck, K. de et al. (2014): Defining a Central Monitoring Capability. Sharing the Experience of TransCelerate BioPharma's Approach, Part 1. In: Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science 48 (5), S. 529–535. DOI: 10.1177/2168479014546335.
Wu, Xiaoru; Carlsson, Martin (2011): Detecting data fabrication in clinical trials from cluster analysis perspective. In: Pharmaceutical statistics 10 (3), S. 257–264. DOI: 10.1002/pst.462.


